Broader Introduction of Renewable Energy Sources
Introduction of Renewable Energy
HEPCO Group is committed to expanding renewable energy to be principal power source for the next generation.
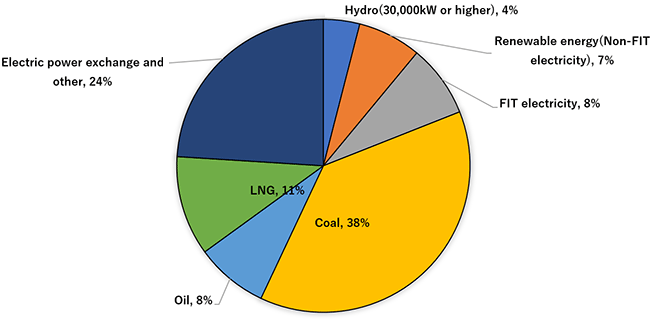
[Composition of HEPCO's electricity sales]
Status of adoption of renewable energy in Hokkaido
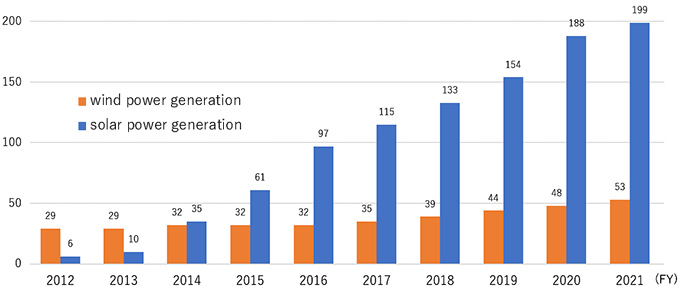
As of March 31 2020, the amount of renewable energy interconnected with systems in Hokkaido was 4,340,000kW, of which hydropower accounted for 1,650,000 kW, wind 480,000 kW, solar 1,880,000 kW, biomass 300,000kW, and geothermal 30,000 kW.
[Amount of wind and solar power interconnected with systems in Hokkaido]
Initiatives Furthering Adoption of Renewable Energies
[HEPCO]
HEPCO has been advancing initiatives for hydroelectric power generation, biomass power generation and other renewable energies that are locally oriented, have little output fluctuation, and little impact on the electric power network.
We are proceeding to verify technologies for maintaining the quality of electric power generated through hydroelectric and photovoltaic systems, and will work to further expand the adoption of these technologies.
- Developing and Increasing Output of Hydroelectric Power Stations
Of the renewable energies, hydroelectric power generation has the capability to generate electricity with less fluctuation than solar or wind power, and is a highly reliable source as hydroelectric power generation technology has been built up over many years.
HEPCO is moving forward to construct new small and medium-sized hydroelectric power stations (output: 30,000 kW and below) and rebuild aging facilities that make use of water resources which have not been previously utilized for power generation. When upgrading water turbines which are a key piece of equipment in existing power stations, we are seeking to replace these with higher efficiency models to increase maximum output (kW).
[Actual and Planned Development of Small and Medium-Sized Hydroelectric Power Stations]
| Power station | Date placed into operation | Output prior (kW) | Output after (kW) | Output increase (kW) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shumarinai | March 2013 | - | 1,120 | - |
| Takinoue-Shibazakura* | December 2013 | 112 | 260 | 148 |
| Yukomanbetsu | June 2014 | - | 710 | - |
| Shin Iwamatsu | January 2016 | 12,600 | 16,000 | 3,400 |
| Kyogoku-Meisui-no-Sato* | October 2016 | - | 410 | - |
| Toya* | June 2018 | 5,500 | 6,400 | 900 |
| Sanru* | April 2019 | - | 1,100 | - |
| Shintoku | June 2022 (Scheduled) | 20,000 | 23,100 | 3,100 |
*Facility owned by HOKUDEN ECO-ENERGY, a HEPCO Group company.
[Actual and Planned Water Turbine Upgrades to Increase Output]
| Power station | Date placed into operation | Output prior (kW) | Output after (kW) | Output increase (kW) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sounkyo | February 2011 | 23,800 | 25,400 | 1,600 |
| Hoheikyo | June 2011 | 50,000 | 51,900 | 1,900 |
| Makunbetsu | February 2012 | 16,400 | 18,000 | 1,600 |
| Hirafu | July 2012 | 11,000 | 12,000 | 1,000 |
| Tomura | March 2015 | 40,000 | 41,300 | 1,300 |
| Shunbetsu | March 2016 | 27,000 | 28,500 | 1,500 |
| Shizunai | September 2017 | 46,000 | 46,700 | 700 |
| Higashi-no-Sawa | April 2018 | 20,000 | 21,000 | 1,000 |
| Kamiakubetsu* | April 2021 (Scheduled) | 4,150 | 4,650 | 500 |
| Abuta* | April 2023 (Scheduled) | 19,500 | 20,790 | 1,290 |
*Facility owned by HOKUDEN ECO-ENERGY, a HEPCO Group company.
[Actual Output Increases Verified by Performance Testing]
| Power station | Date placed into operation | Output prior (kW) | Output after (kW) | Output increase (kW) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Toyoura* | March 2013 | 3,400 | 3,500 | 100 |
| Aibetsu | October 2015 | 5,500 | 5,600 | 100 |
| Shibinai | October 2015 | 1,300 | 1,600 | 300 |
| Toyama | January 2016 | 10,000 | 10,200 | 200 |
| Iwachishi | April 2016 | 13,500 | 14,300 | 800 |
| Okusaru | April 2018 | 15,000 | 15,800 | 800 |
*Facility owned by HOKUDEN ECO-ENERGY, a HEPCO Group company.
- Biomass Power Generation Project Participation and Research & Development
HEPCO is participating in a biomass power generation project utilizing the region's forestry resources. Hokkaido Biomass Energy Co., Ltd., in which HEPCO has a stake, has started construction of a new power generation facility in Tobetsu town.
In addition, HEPCO has joined a fund whose investment structure is based on the concept of "local consumption of locally-produced energy and locally-procured financing" (investing in solar power generation facilities in Iwamizawa and Kushiro cities).
[HEPCO Network]
- Activities aimed at expansion of renewable energy
Greater accuracy in forecasting renewable energy power generation
To reliably and efficiently manage demand and supply, the Renewable Energy Forecast System was introduced inFY2017 which forecasts solar and wind power generation.
In FY2018, a new forecasting method was developed that takes into account snow buildup on solar panels. We have been confirming its effectiveness and otherwise fine-tuning the system by verifying the forecasting technology through actual use and then making improvements.Demonstration test with TEPCO Power Grid for introducing more wind power generation
One initiative toward our goal of expanding wind power generation is the demonstration test that we are conducting with TEPCO Power Grid using current interregional transmission lines (launched in January 2018).
This demonstration test makes use of TEPCO's adjustment capacity across inter-regional transmission lines. For this test, we solicited approximately 200,000 kW of wind power in December 2011. (In February 2017, we solicited an additional 63,500 kW, a shortfall that occurred due to withdrawals and other departures.)Large-scale storage battery system demonstration project
Sumitomo Electric Industries, Ltd. applied for and was selected to conduct the "FY2013 Large-Scale Storage Battery System Demonstration Project" implemented by the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry for the purpose of demonstrating the capacity to adjust to fluctuations in output from renewable energy power sources and develop optimal control technology.
At the Minami Hayakita Substation (Abira town, Yufutsu district), a large capacity redox flow battery (rated output: 15MW; storage capacity: 60 MWh [15 MW*4 hours]) has been installed. Control technology was also developed, battery performance evaluated, and other technology verified. In January 2019, the demonstration test was completed. The knowledge gained from this assessment has been made use of in reviewing wind power offerings that utilize system storage batteries.Wind power offerings utilizing system storage batteries
We have endeavored to solicit wind power offerings of 1 million kW (Phase I: 600,000 kW; Phase II: 400,000 kW) intended to jointly defray the costs associated with the system storage batteries. In Phase I, 15 applications from operators, expressing their desire for power system interconnection, were ultimately received, which amounted to 162,000 kW, and 17,000 kW-3h (51,000 kWh) of system storage batteries installed. We are currently engaged in construction and other work in order to commence storage battery operation for Phase I in FY2023. For the remaining 438,000 kW, additional wind power solicitations (balance of Phase I capacity) will be held to augment the adoption of renewable energies.
Power grid development demonstration project for wind power generation
As part of our efforts to increase renewable energies, we have invested and provided technical assistance to North Hokkaido Wind Energy Transmission Corporation, a special-purpose company chosen for this project.
The project began with the selection of powerline routes and other research on the development potential. Viability evaluations were taken into account and a decision already made to go ahead with commercialization (powerline development and operation).
The project has carried out construction work and other preparations with the aim of starting operation of a transmission and conversion facility in FY2023.Participation in NEDO demonstration project related to "Japan Connect & Manage"
After an application was filed as part of a consortium led by TEPCO Power Grid for a demonstration project, which was solicited by the New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO), seeking to increase the adoption of renewable energies, it was announced that the consortium had been accepted on June 23, 2020.
Through participation in this project, we will be able to further our knowledge of the application of non-firm connections, which will make it possible to introduce renewables even in the Hokkaido area in the future, so that we can achieve such grid management.